-
Feed de notícias
- EXPLORAR
-
Páginas
-
Grupos
-
Eventos
-
Reels
-
Blogs
-
Marketplace
-
Jobs
Spot Resistance Welder: Enhancing Precision and Efficiency in Industrial Manufacturing
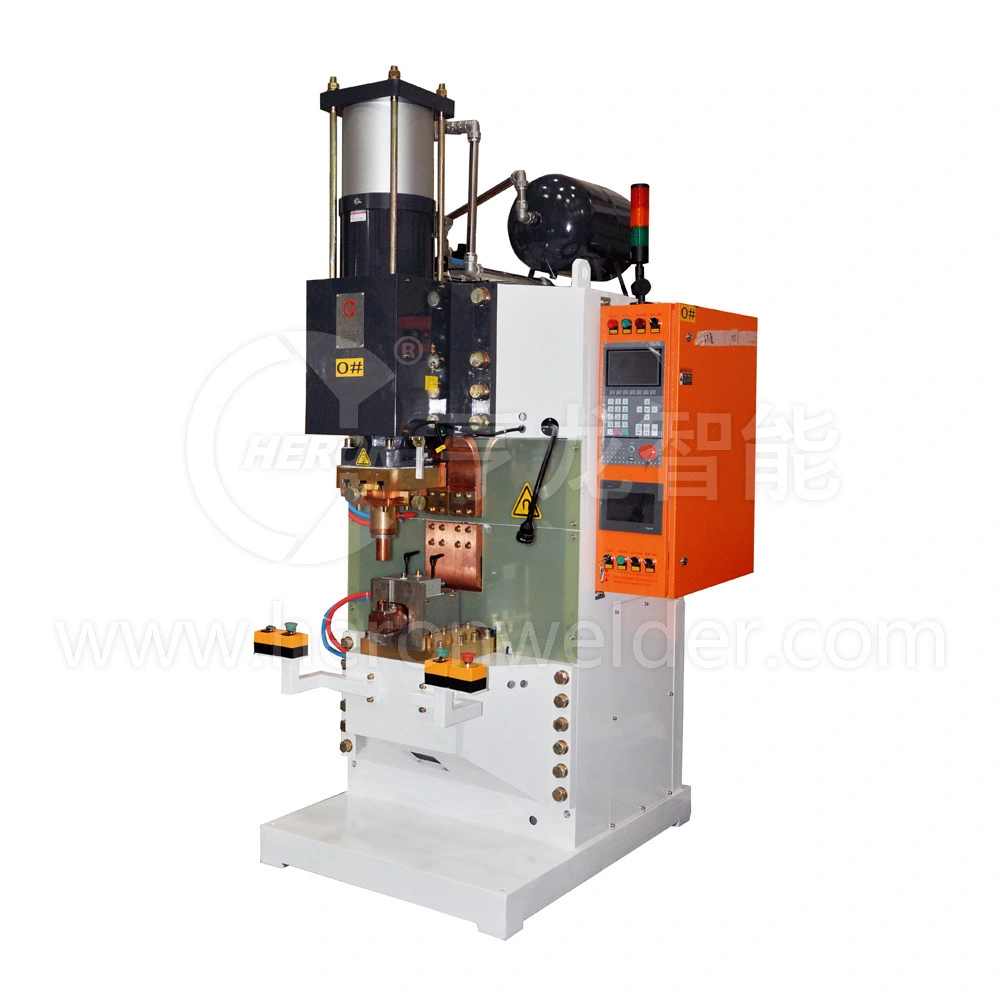

In modern manufacturing, efficiency, consistency, and precision are non-negotiable. For OEMs, automation integrators, and production engineers, achieving strong, repeatable welds in sheet metal assemblies is critical. A spot resistance welder is a cornerstone technology that delivers reliable, high-speed welding for automotive, electronics, appliance, and metal fabrication industries. Heron Welder, a global leader in industrial welding and metal-joining solutions, offers a comprehensive range of spot resistance welding machines designed to optimize production lines while ensuring superior quality.
In this guide, we’ll explore the principles, applications, advantages, and best practices of spot resistance welding, highlighting how Heron’s solutions help manufacturers achieve operational excellence.
What is a Spot Resistance Welder?
A spot resistance welder is a type of resistance welding machine that joins two or more metal sheets by applying heat generated from electrical resistance at the contact point. The process is simple yet highly effective:
-
Metal sheets are placed between copper electrodes.
-
A controlled electric current passes through the electrodes, generating heat at the interface due to electrical resistance.
-
Pressure from the electrodes forges a strong, localized weld.
This technique is ideal for joining sheet metals quickly without introducing filler material, flux, or extensive post-processing.
How Spot Resistance Welding Works
The working principle of spot resistance welding relies on Joule heating:
-
Current Flow: High current passes through the metal sheets at the contact point.
-
Resistance Heating: The electrical resistance converts electrical energy into heat, localized at the weld nugget.
-
Pressure Application: Mechanical pressure from electrodes consolidates the molten material into a solid weld.
-
Cooling Phase: After the current is stopped, the welded joint cools under pressure, ensuring strength and dimensional stability.
Heron’s MFDC and capacitor discharge spot welders enhance this process by offering precise control over current, pressure, and timing, enabling high-quality welds even on thin or sensitive materials.
Key Applications of Spot Resistance Welding
Spot resistance welding is widely used across industries for applications that demand speed, repeatability, and minimal post-processing:
-
Automotive Manufacturing: Body panels, chassis components, battery packs for electric vehicles.
-
Appliance Production: Washing machines, refrigerators, and air conditioners.
-
Electronics and Electrical Equipment: Battery tabs, transformers, and metal housings.
-
Metal Furniture & HVAC Systems: Sheet metal assemblies and ducting connections.
Heron Welder provides tailored solutions for each application, from standalone spot welders to fully automated production lines, helping factories increase throughput without compromising weld integrity.
Spot Resistance Welder vs. Other Welding Methods
Understanding how spot welding compares with other metal-joining techniques helps manufacturers make informed decisions:
| Feature | Spot Resistance Welding | MIG Welding | TIG Welding |
|---|---|---|---|
| Speed | High | Moderate | Low |
| Material Thickness | Thin to medium | Medium to thick | Thin to medium |
| Automation Friendly | Excellent | Moderate | Limited |
| Heat Affected Zone | Minimal | Moderate | Low |
| Filler Material | Not required | Required | Required |
Heron’s advanced spot resistance welders combine precision and speed, making them a preferred choice for automated assembly lines where consistent quality and cycle times are critical.
Best Practices for Spot Resistance Welding
To maximize efficiency and ensure high-quality welds, manufacturers should follow these best practices:
-
Correct Electrode Selection: Choose electrodes suitable for material type and thickness to avoid premature wear or inconsistent welds.
-
Proper Maintenance: Regular cleaning and shaping of electrodes maintain consistent welding quality.
-
Optimal Current and Pressure Settings: Adjust parameters based on material properties to avoid overburning or weak welds.
-
Process Monitoring: Implement real-time monitoring systems, like Heron’s advanced controllers, to ensure every weld meets quality standards.
-
Material Preparation: Ensure clean, oxide-free surfaces for optimal electrical contact and weld strength.
Heron’s team supports manufacturers in designing customized welding schedules and automation integration to streamline production and minimize defects.
Why Choose Heron Spot Resistance Welders
Heron Welder stands out as a global leader in industrial welding solutions for several reasons:
-
Advanced Technology: MFDC, capacitor discharge, and servo-controlled spot welders for precise, repeatable welds.
-
Automation Expertise: Integration-ready systems for robotic cells and high-volume production lines.
-
Global Support: Installation, training, and maintenance services worldwide.
-
Customized Solutions: Machines tailored for material types, thicknesses, and production speeds.
Manufacturers choosing Heron benefit from reduced cycle times, lower operational costs, and superior weld quality, ensuring a measurable ROI.
FAQs About Spot Resistance Welders
1. What materials can a spot resistance welder join?
Spot welders are ideal for mild steel, stainless steel, nickel, and some aluminum alloys, depending on the welder’s current capacity and electrode type.
2. How thick can the metal sheets be?
Most standard spot welders handle sheets from 0.3 mm to 6 mm. Advanced MFDC machines can weld even thicker sections with precision.
3. Can spot welding be automated?
Yes, Heron offers fully automated spot welding cells integrated with robotic arms for high-volume production.
4. What maintenance is required for spot welders?
Regular electrode cleaning, tip dressing, and controller calibration ensure consistent weld quality and prolong machine life.
5. How does a spot welder differ from a seam welder?
Spot welders create discrete welds, while seam welders produce continuous welds along a joint. Both use resistance heating principles but serve different applications.
Conclusion: Optimize Your Production with Heron
A spot resistance welder is essential for manufacturers seeking fast, reliable, and precise metal joining. Heron Welder combines advanced technology, automation readiness, and global expertise to deliver solutions that improve production efficiency, reduce costs, and ensure weld quality.
For OEMs, automation integrators, and factory decision-makers, partnering with Heron means access to customized welding systems, expert consultation, and ongoing support to optimize your production lines.
Request a quote today or consult Heron’s team to explore tailored spot resistance welding and automation solutions that elevate your manufacturing capabilities.
- Arte
- Causas
- Artesanía
- Bailar
- Bebidas
- Película
- Fitness
- Alimento
- Juegos
- Jardinería
- Salud
- Hogar
- Literatura
- Musica
- Redes
- Otro
- Fiesta
- Religión
- Compras
- Deportes
- Teatro
- Bienestar