-
Newsfeed
- ERKUNDEN
-
Seiten
-
Gruppen
-
Veranstaltungen
-
Reels
-
Blogs
-
Marktplatz
-
Jobs
Nanosatellite & Microsatellite Market Report by Mass, Component & Use 2025
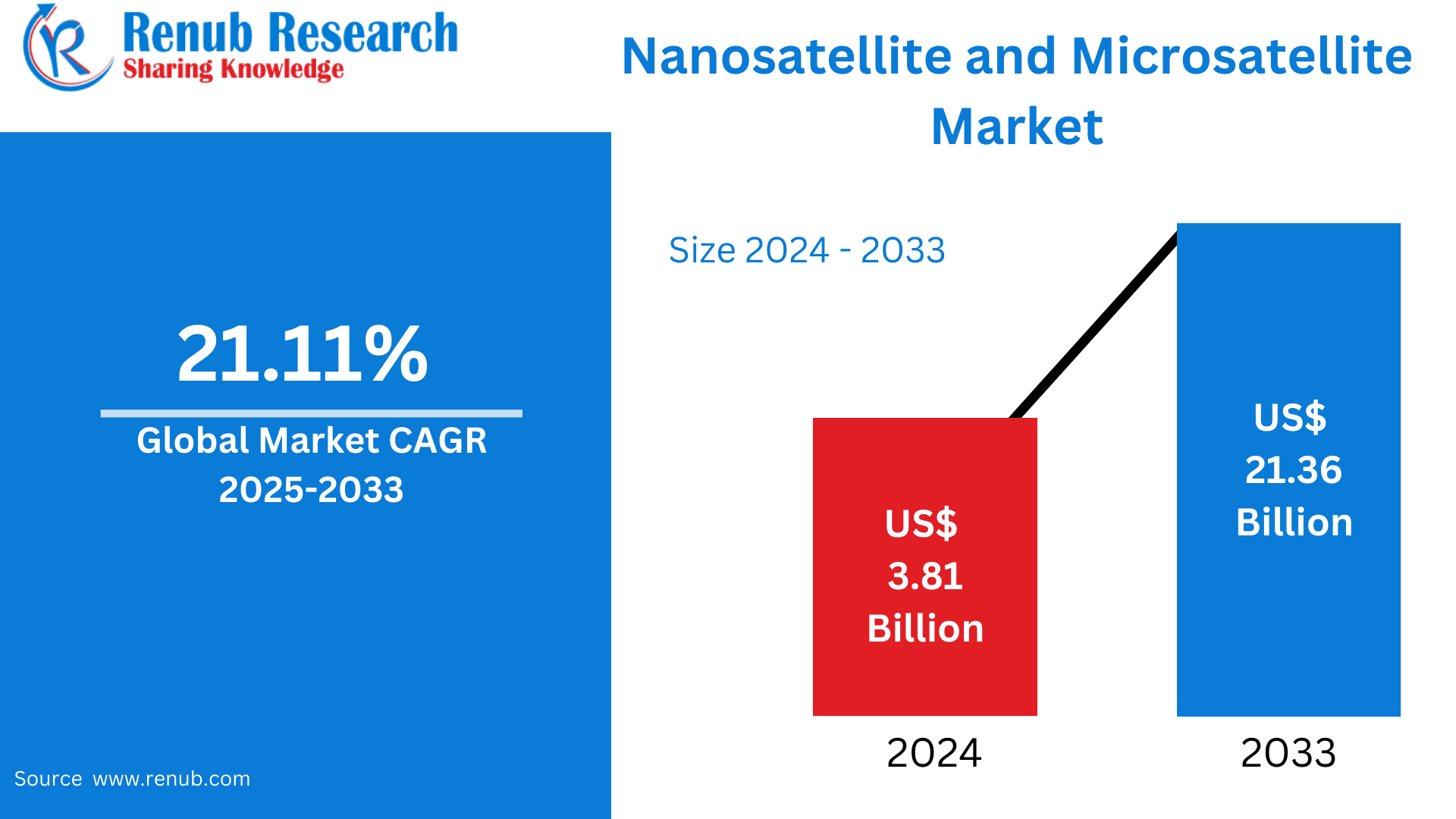
Nanosatellite and Microsatellite Market Size and Forecast 2025–2033
According To Renub Research global nanosatellite and microsatellite market is undergoing rapid transformation and expansion, driven by accelerating commercialization of space, growing demand for Earth observation data, rising Internet of Things (IoT) connectivity requirements, and continuous technological innovation in satellite miniaturization. The market was valued at US$ 3.81 billion in 2024 and is projected to reach US$ 21.36 billion by 2033, expanding at a robust compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 21.11% from 2025 to 2033.
Nanosatellites and microsatellites have emerged as cost-effective, flexible, and scalable alternatives to traditional large satellites. Their ability to support diverse missions—including communication, environmental monitoring, scientific research, navigation, and defense—has positioned them as essential components of the modern space ecosystem. As access to space becomes increasingly democratized, small satellites are redefining how governments, enterprises, and academic institutions deploy space-based services.
Download Free Sample Report:https://www.renub.com/request-sample-page.php?gturl=nanosatellite-microsatellite-market-p.php
Global Nanosatellite and Microsatellite Industry Overview
Nanosatellites, commonly referred to as CubeSats, are small satellites weighing between 1 kg and 10 kg, typically built in standardized cubic units measuring approximately 10 cm per side. Despite their compact size, nanosatellites integrate essential subsystems such as power generation, onboard computing, attitude control, and communication modules. These capabilities allow them to perform targeted missions, including technology demonstrations, academic research, and basic Earth observation.
Microsatellites, which range from 10 kg to 100 kg, offer greater payload capacity and operational flexibility compared to nanosatellites. Their larger size enables the integration of more advanced sensors, higher-resolution imaging systems, and stronger communication payloads. Microsatellites are widely used in applications such as Earth observation, remote sensing, telecommunications, and reconnaissance, where higher data quality and longer mission lifetimes are required.
Compared to traditional large satellites, nanosatellites and microsatellites offer significant advantages, including lower manufacturing and launch costs, shorter development cycles, and the ability to deploy large constellations. Their compatibility with rideshare launches and existing satellite networks further enhances deployment efficiency. These advantages have fueled widespread adoption across commercial, government, and defense sectors, contributing to rapid market growth.
Market Dynamics and Growth Drivers
Expanding Demand for Cost-Effective Satellite Solutions
One of the primary drivers of the nanosatellite and microsatellite market is the growing demand for affordable and rapid satellite deployment. Traditional satellite missions often require substantial capital investment and long development timelines, limiting participation to a small number of nations and large organizations. In contrast, small satellites significantly reduce financial and technical barriers, enabling startups, universities, and emerging space nations to access space-based capabilities.
The increasing availability of shared and rideshare launch services has further lowered launch costs, making small satellite missions economically viable. This affordability has accelerated innovation across sectors such as communication, meteorology, environmental monitoring, and scientific research. As organizations seek faster and more flexible solutions, nanosatellites and microsatellites are becoming preferred alternatives to conventional satellite platforms.
Rising Applications in Earth Observation and Remote Sensing
Earth observation and remote sensing represent some of the most significant application areas for nanosatellites and microsatellites. These satellites provide near-real-time data on climate change, land use, agriculture, urban development, disaster management, and natural resource monitoring. Their ability to revisit specific geographic locations frequently offers a major advantage over large satellites, which typically have longer revisit cycles.
Small satellite constellations enable continuous monitoring and rapid data delivery, supporting time-sensitive applications such as disaster response, wildfire detection, flood monitoring, and precision agriculture. Governments, research institutions, and commercial enterprises increasingly rely on this data to support policy decisions, operational planning, and business intelligence. As demand for timely and high-resolution geospatial data grows, the market for nanosatellites and microsatellites continues to expand globally.
Technological Advancements in Miniaturization
Technological progress in miniaturization has dramatically enhanced the capabilities of nanosatellites and microsatellites. Advances in microelectronics, sensors, propulsion systems, onboard processing, and power management have enabled small satellites to perform complex missions that were once exclusive to large spacecraft.
Modern nanosatellites can now support high-speed data transmission, autonomous operations, precision navigation, and advanced imaging. Modular satellite architectures, particularly CubeSat platforms, have streamlined design and manufacturing processes, enabling mass production and faster deployment. These innovations have attracted increased investment from commercial players and research organizations, reinforcing long-term market growth.
Challenges in the Nanosatellite and Microsatellite Market
Limited Payload Capacity and Performance Constraints
Despite technological improvements, nanosatellites and microsatellites face inherent limitations related to payload capacity, power availability, and operational lifespan. Their small size restricts the complexity and scale of onboard instruments, which can limit sensor resolution, data throughput, and mission duration compared to larger satellites.
These constraints pose challenges for applications requiring high-resolution imagery, large data volumes, or extended operational life. As mission requirements become more data-intensive, manufacturers must balance performance with size and cost limitations. Continued innovation in energy-efficient components, advanced materials, and optimized mission design is essential to overcoming these challenges.
Orbital Congestion and Space Debris Risks
The rapid deployment of large nanosatellite and microsatellite constellations has intensified concerns over orbital congestion and space debris. Thousands of small satellites operating in low Earth orbit increase the risk of collisions, which can generate debris and threaten the sustainability of space operations.
Many small satellites lack advanced propulsion systems for collision avoidance and controlled deorbiting, making end-of-life management a critical issue. Regulatory authorities and industry stakeholders are increasingly focused on developing debris mitigation strategies, satellite tracking systems, and responsible launch practices. Without effective coordination and regulation, orbital congestion could limit future deployment opportunities and raise operational risks.
Regional Market Overview
North America
North America leads the global nanosatellite and microsatellite market due to strong technological capabilities, significant government funding, and a mature commercial space ecosystem. The region benefits from advanced launch infrastructure, a supportive regulatory environment, and a high concentration of aerospace companies and startups. Demand is driven by defense, Earth observation, communication, and research applications.
Europe
Europe represents a major market for nanosatellites and microsatellites, supported by government-backed space programs, academic research, and industrial collaboration. The region emphasizes innovation, sustainability, and dual-use satellite technologies. Participation in multinational space initiatives strengthens Europe’s competitive position in the global market.
Asia-Pacific
Asia-Pacific is one of the fastest-growing regions, fueled by increasing investments in space programs, rising private sector participation, and growing demand for satellite-based services. Countries in the region are leveraging small satellites for communication, disaster management, agriculture, and national security. Cost-effective manufacturing and launch capabilities further enhance regional growth prospects.
Latin America
Latin America is gradually adopting nanosatellite and microsatellite technologies to support environmental monitoring, telecommunications, and educational initiatives. Government partnerships and international collaboration play a key role in market development, although limited infrastructure remains a challenge.
Middle East and Africa
The Middle East and Africa are emerging markets for small satellites, driven by national space strategies, infrastructure development, and investments in innovation. Small satellite programs are increasingly used for Earth observation, climate monitoring, and technological capacity building, contributing to long-term regional growth.
Country-Level Market Insights
United States
The United States dominates the global nanosatellite and microsatellite market through strong government support, substantial private investment, and advanced space infrastructure. Small satellites are widely used for defense, Earth observation, scientific research, and commercial data services. A dynamic startup ecosystem and availability of launch services support rapid market expansion and technological leadership.
Germany
Germany’s nanosatellite and microsatellite market benefits from strong engineering expertise, academic research, and government-supported space initiatives. The country focuses on Earth observation, climate monitoring, and communication missions, with an emphasis on innovation and sustainability. Collaboration between public institutions and private enterprises enhances market competitiveness.
India
India’s market is expanding rapidly due to cost-efficient satellite manufacturing, increasing private sector involvement, and supportive government policies. Small satellites are used extensively for Earth observation, education, communication, and disaster management. India’s affordable launch capabilities make it an attractive partner for international satellite deployments.
United Arab Emirates
The UAE has emerged as a regional leader in nanosatellite and microsatellite development, driven by strategic investments in space technology and innovation. National space programs focus on Earth observation, scientific research, and capacity building. Government support and international collaboration continue to strengthen the UAE’s position in the global space economy.
Market Segmentation
By Satellite Mass
· Nanosatellite (1 kg to 10 kg)
· Microsatellite (10 kg to 100 kg)
By Component
· Hardware
· Software and Data Processing
· Space Services
· Launch Services
By Application
· Communication
· Earth Observation and Remote Sensing
· Scientific Research
· Biological Experiments
· Technology Demonstration and Verification
· Academic Training
· Mapping and Navigation
· Reconnaissance
· Others
By End-Use Sector
· Government
· Civil
· Commercial
· Defense
· Energy and Infrastructure
· Others
By Region
· North America
· Europe
· Asia-Pacific
· Latin America
· Middle East & Africa
Competitive Landscape
The nanosatellite and microsatellite market is highly competitive and innovation-driven. Key players focus on satellite miniaturization, constellation deployment, launch integration, and data analytics services. Strategic partnerships, government contracts, and technological advancements play a crucial role in shaping competitive positioning.
Each major company is analyzed across multiple dimensions, including business overview, leadership, recent developments, SWOT analysis, revenue performance, and strategic outlook. Continuous investment in research and development remains essential for maintaining competitiveness in this rapidly evolving market.
Conclusion
The global nanosatellite and microsatellite market is set for exceptional growth through 2033, driven by cost efficiency, expanding commercial space activity, and increasing demand for real-time data and connectivity. While challenges related to payload limitations and orbital congestion persist, ongoing technological advancements and regulatory efforts are expected to support sustainable market expansion. As space becomes more accessible and integrated into everyday applications, nanosatellites and microsatellites will play a central role in shaping the future of the global space economy.
- Arte
- Causas
- Artesanía
- Bailar
- Bebidas
- Película
- Fitness
- Alimento
- Juegos
- Jardinería
- Salud
- Hogar
- Literatura
- Musica
- Redes
- Otro
- Fiesta
- Religión
- Compras
- Deportes
- Teatro
- Bienestar